The content on our website is provided solely for general informational purposes. It should not be considered, nor is it intended to provide advice or recommendations for the purchase, sale, or trade of any products or services. Importantly, the information presented does not constitute an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any product.
Please be aware that the availability of our products may vary across different markets due to regulatory restrictions or other considerations. Consequently, not all products or services may be available in your region or country. For specific inquiries regarding the availability and pricing of any product, please contact us at sales@noctiluca.eu.
General information
-
Name:
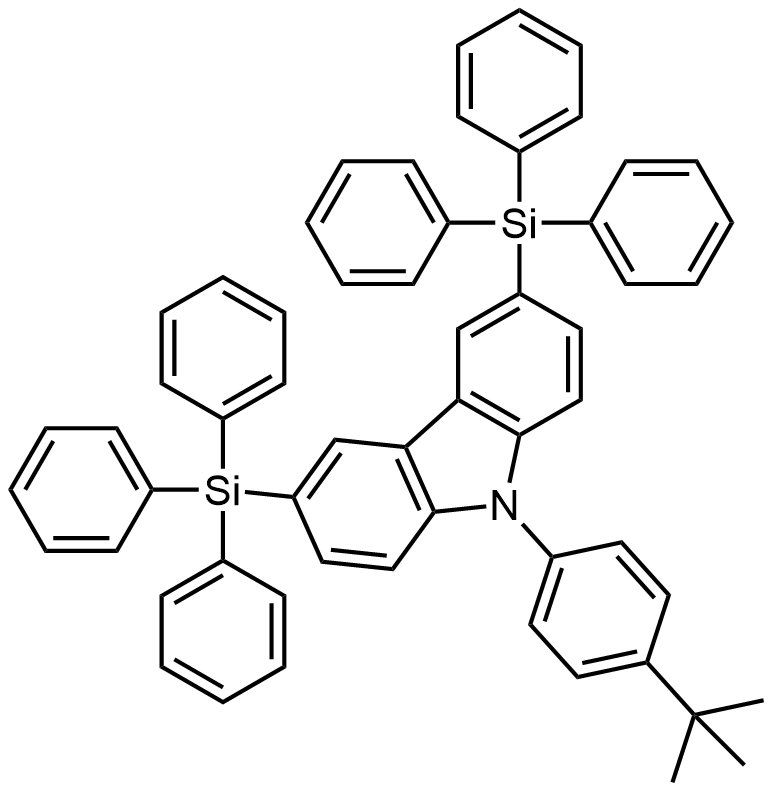
CzSi
-
Full name:
9-(4-tert-Butylphenyl)-3,6-bis(triphenylsilyl)-9H-carbazole
-
CAS number:
898546-82-2
-
Chemical formula:
C58H49NSi2
-
Molecular weight:
816.19 g/mol
-
Absorption:
λmax = 275 nm in DCM
-
Photoluminescence:
λmax = 354 nm in DCM
-
HOMO/LUMO:
HOMO = 6.0 eV, LUMO = 2.5 eV
-
Synonyms:
-
-
Classification:
Organic light-emitting diodes, TADF materials, Hole transport layer materials (HTL), PHOLED materials
-
Purity:
Sublimed: >99.0% (HPLC)
-
Melting point:
TGA: 354 °C
-
Appearance:
Off-white powder/crystals
CzSi Specification: Unlocking the Potential in OLED Technology
The landscape of Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (OLEDs) is in a constant state of flux, driven by the development of new materials and compounds. Among these, CzSi stands as a pivotal element in the OLED technology stack.
Understanding CzSi
CzSi is a complex compound with a unique structure that makes it an invaluable material in organic electronic devices. Its full name is 9-(4-tert-Butylphenyl)-3,6-bis(triphenylsilyl)-9H-carbazole. This compound is classified under various categories such as Organic Light-Emitting Diodes, TADF materials, Hole Transport Layer materials (HTL), and PHOLED materials.
Key Features of CzSi
- Exciplex Forming Nature: One of the most advanced features of CzSi is its ability to form exciplexes. This property is crucial for the development of next-generation OLEDs, particularly in the area of TADF (Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence) OLEDs.
- Hole Transport Layer Material: CzSi is extensively used as a material in Hole Transport Layers (HTL). This systematic approach ensures that OLEDs operate efficiently and have extended lifetimes.
- Versatile Host Material: CzSi serves as a host material for various types of OLEDs, including those that utilize phosphorescent materials. Its versatility increases its value in the OLED material stack.This material is extensively employed as a TADF host for achieving blue electrophosphorescence, making it one of the most commonly utilized choices in this regard.
- Stability: This material maintains the substantial triplet energy characteristic of carbazole, but it demonstrates significantly improved stability in both morphology and electrochemistry when compared to other host materials based on carbazole.
The Role of CzSi in Modern OLEDs
In today’s OLED landscape, there is a huge demand for materials that offer high efficiency, durability, and reduced energy consumption. CzSi, with its unique attributes, is optimally positioned to meet these demands. Its role as a Hole Transport Layer material and its ability to form exciplexes contribute to the development of more energy-efficient and long-lasting OLED devices.
Conclusion
The OLED industry is ever-evolving, and the need for efficient, durable materials is continually increasing. CzSi, with its unique properties and extensive applications, is set to play a significant role in shaping the future of OLED technology. As research progresses and technology advances, it’s clear that CzSi will find more and more applications in organic electronic devices.