The content on our website is provided solely for general informational purposes. It should not be considered, nor is it intended to provide advice or recommendations for the purchase, sale, or trade of any products or services. Importantly, the information presented does not constitute an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any product.
Please be aware that the availability of our products may vary across different markets due to regulatory restrictions or other considerations. Consequently, not all products or services may be available in your region or country. For specific inquiries regarding the availability and pricing of any product, please contact us at sales@noctiluca.eu.
General information
-
Name:
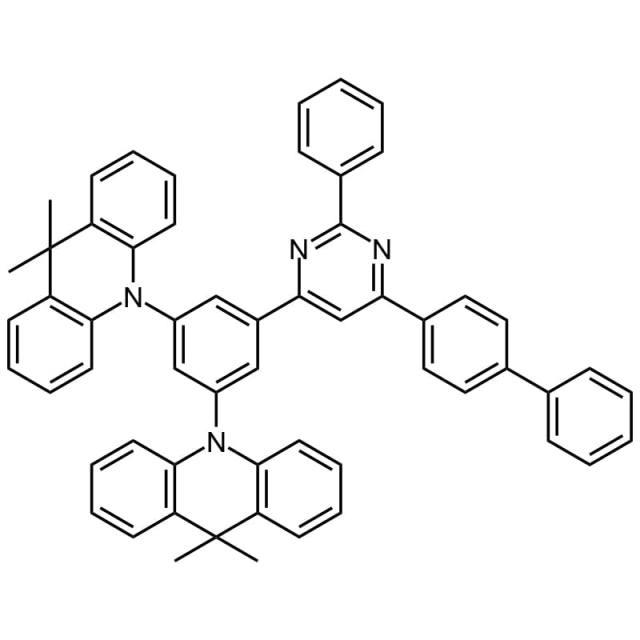
DMAC-BPP
-
Full name:
10,10′‐[5‐(6‐[1,1′‐Biphenyl]‐4‐yl‐2‐phenyl‐4‐pyrimidinyl)‐1,3‐phenylene]bis[9,10‐dihydro‐9,9‐dimethyl‐acridine]
-
CAS number:
1836192-40-5
-
Chemical formula:
C58H46N4
-
Molecular weight:
788.01 g/mol
-
Absorption:
λmax = 282 nm
-
Photoluminescence:
λmax = 496 nm
-
HOMO/LUMO:
HOMO = 5.4 eV, LUMO = 2.5 eV
-
Synonyms:
BPP-DMAC, Acridine, 10,10'-(5-(6-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-phenylpyrimidin-4-yl)-1,3-phenylene)bis(9,9-dimethyl-9,10-dihydroacridine)
-
Classification:
Organic light-emitting diodes, Emmiting layer materials (EML), TADFmaterials, Blue fluorescent dopant materials, Host materials, PHOLED materials
-
Purity:
Sublimed: >99.0% (HPLC)
-
Melting point:
Tg = 220 °C
-
Appearance:
Light yellow powder/crystals
DMAC-BPP Specification: The Cutting-Edge Emitter in 3rd Generation OLEDs
The ever-evolving field of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) is enriched by a multitude of materials and compounds. Among these, DMAC-BPP fully known as 10,10′‐[5‐(6‐[1,1′‐Biphenyl]‐4‐yl‐2‐phenyl‐4‐pyrimidinyl)‐1,3‐phenylene]bis[9,10‐dihydro‐9,9‐dimethyl‐acridine] stands as a pivotal element in the OLED technology stack.
Understanding DMAC-BPP
DMAC-BPP is a complex molecule composed of two 9,9-dimethyl-9,10-dihydroacridine units, substituted to a benzene ring, which is further coupled with a phenyl pyrimidine derivative. This compound is particularly significant in the realm of organic electronic devices, including OLEDs.
Key Features of DMAC-BPP
- Efficient TADF Emitter: DMAC-BPP serves as an efficient Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence (TADF) emitter, with an emission wavelength of 496 nm, corresponding to the blue-green color of light.
- Versatile Host Material in PhOLEDs: The compound is also employed as a host material in phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes (PhOLEDs), enhancing their overall performance.
- Blue Fluorescent Dopant Material: DMAC-BPP’s unique molecular structure and emission properties make it a suitable blue fluorescent dopant material, adding versatility to its applications.
The Role of DMAC-BPP in Advanced OLEDs
In the current OLED technology landscape, the quest for materials that offer high efficiency, durability, and low energy consumption is relentless. DMAC-BPP, with its unique molecular structure and emission properties, aligns perfectly with these prerequisites. Its role as an efficient TADF emitter and host material in PhOLEDs ensures that OLEDs not only function optimally but also have an extended lifespan.
Conclusion
The realm of OLED technology is perpetually advancing, driven by an insatiable demand for materials that exhibit both high performance and longevity. DMAC-BPP, distinguished by its unique molecular architecture and photophysical attributes, is well-positioned to make a substantial impact on the future trajectory of OLED applications. Its efficacy as a TADF emitter and its versatility as a host material in PhOLEDs indicate that, as scientific research deepens and technological capabilities expand, DMAC-BPP is likely to see a broader spectrum of applications in the field of organic electronics.