The content on our website is provided solely for general informational purposes. It should not be considered, nor is it intended to provide advice or recommendations for the purchase, sale, or trade of any products or services. Importantly, the information presented does not constitute an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any product.
Please be aware that the availability of our products may vary across different markets due to regulatory restrictions or other considerations. Consequently, not all products or services may be available in your region or country. For specific inquiries regarding the availability and pricing of any product, please contact us at sales@noctiluca.eu.
General information
-
Name:
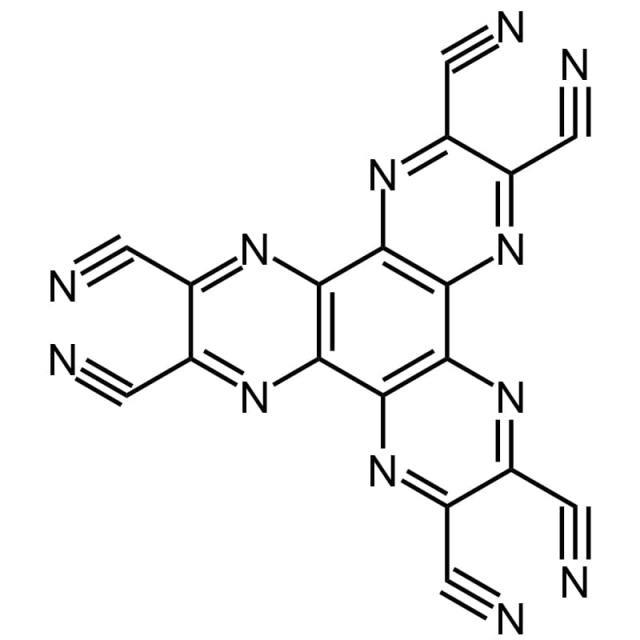
HATCN
-
Full name:
1,4,5,8,9,11-Hexaazatriphenylenehexacarbonitrile
-
CAS number:
105598-27-4
-
Chemical formula:
C18N12
-
Molecular weight:
384.27 g/mol
-
Absorption:
λmax = 282 nm, 321 nm in DCM
-
Photoluminescence:
λmax = 422 nm in DCM
-
HOMO/LUMO:
HOMO = 7.5 eV, LUMO = 4.4 eV
-
Synonyms:
HAT-CN6, Dipyrazino[2,3-f:2',3'-h]quinoxaline-2,3,6,7,10,11-hexacarbonitrile
-
Classification:
Organic light-emitting diodes, Polymer light-emitting diode materials, Charge-generation layer materials (CGL), Hole injection layer materials (HIL), Perovskite solar cells
-
Purity:
Sublimed: >99%
-
Melting point:
430 °C (0.5% weight loss)
-
Appearance:
Dark yellow powder/crystals
HATCN Specification: The Forefront of Organic Electronics and Solar Cells
The ever-advancing field of organic electronics and solar cells is enriched by a multitude of materials, each contributing unique properties and functionalities. Among these, HATCN officially known as 1,4,5,8,9,11-Hexaazatriphenylenehexacarbonitrile stands out as a pivotal material.
Understanding HATCN
HATCN is a complex organic molecule consisting of a benzene ring and three pyrazine rings, all substituted with cyano groups. This unique configuration renders the molecule rigid, planar, and electron-deficient. These characteristics are instrumental in its widespread application in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and organic solar cells (OPVs).
Key Features of HATCN
- Versatility in Layer Applications: HATCN’s electron-deficient nature and planar structure make it an ideal candidate for various layer applications, including hole transport layers (HTL) and charge-generation layers (CGL) in OLEDs and OPVs.
- Hole Injection Layer Material: The molecule’s rigidity and planar structure facilitate its use as a hole injection layer material (HIL), enhancing the efficiency and stability of OLEDs and OPVs.
- Electron-Deficient Nature: The electron-deficient nature of HATCN makes it a valuable material for charge-generation layers, offering increased efficiency in both OLEDs and perovskite solar cells.
The Role of HATCN in Advanced Organic Electronics
In the current landscape of organic electronics, the demand for materials that offer high efficiency, durability, and low energy consumption is incessant. HATCN, with its unique molecular structure and electron-deficient nature, aligns seamlessly with these prerequisites. Its role as a versatile layer material in OLEDs, PLEDs and OPVs ensures not only optimal functionality but also extended device longevity.
Conclusion
The organic electronics sector is in a perpetual state of innovation, driven by the quest for materials that offer both efficiency and durability. HATCN, with its unique molecular structure and electron-deficient nature, is poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of this industry. As research advances and technology matures, HATCN is anticipated to find an expanding array of applications, particularly as a versatile layer material in OLEDs and OPVs.