December 2023
Blog post by Noctiluca
In the world of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), a groundbreaking technology has emerged that promises to push the boundaries of energy efficiency and display quality. This technology is known as Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence (TADF) and Noctiluca is its designer and producer. We are working on the commercial deployment of the new (3rd, 4th and 5th) generation of our proprietary emitters dedicated to both PVD and IJP applications.
TADF has rapidly gained momentum in recent years, and its potential to revolutionize OLEDs is capturing the attention of scientists, engineers, and manufacturers alike. In this article, we will delve into the world of TADF, exploring not only its principles, but also its environmental benefits and the impact it is poised to make on the future of lighting and display technology.
Understanding TADF
TADF, or Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence, is a phenomenon that occurs in certain organic materials used in OLEDs. Like phosphorescence, TADF allows up to 100% of the current-excited emitter molecules to be used to emit light, and like traditional fluorescent emitters, it does not contain expensive heavy metals in its structure. The key to TADF’s success lies in its ability to convert triplet excitons, which are typically non-emissive, into singlet excitons, which emit light.
OLED emitters:
powder-like chemical compounds that emit light when exposed to electricity. They arefundamental basis of any OLED display and determine its performance, such as color, contrast and durability
Eco-benefits
As the world becomes increasingly mindful of sustainability and environmental responsibility, TADF’s advantages in this area make it a compelling option for the future of lighting and display technology. The key benefit of using TADF emitters is that there is no need to build new production lines in factories, just swap one material in a powder form for another – prolonging the lifecycle of currently used setups.
Why else TADF is better for the environment compared to traditional OLED technologies?
Energy efficiency: TADF-based OLEDs are significantly more energy-efficient than traditional OLEDs. This means that they consume less electricity to produce the same level of brightness. Lower energy consumption translates into reduced greenhouse gas emissions when the electricity is generated from fossil fuels. Additionally, it extends the battery life of portable devices, reducing the frequency of recharging and the associated energy consumption.
Resource conservation: TADF materials often use more abundant and less resource-intensive organic compounds. Traditional OLEDs sometimes rely on rare earth and precious materials, which can have significant environmental impacts during mining and extraction. TADF’s reliance on fully organic compounds contributes to resource conservation and reduces the ecological footprint of OLED production.
Longer lifespan: OLEDs utilizing TADF materials tend to have longer lifespans compared to traditional OLEDs. This means that electronic devices and lighting fixtures incorporating TADF OLEDs will need less frequent replacement, reducing electronic waste. Longer-lasting products are generally more sustainable as they require fewer resources for manufacturing and disposal.
Reduced toxicity: TADF materials often contain fewer toxic or hazardous substances than some traditional OLED materials. Reducing the use of toxic materials is crucial for the environment, as it minimizes the risk of pollution during the manufacturing process and disposal of electronic devices.
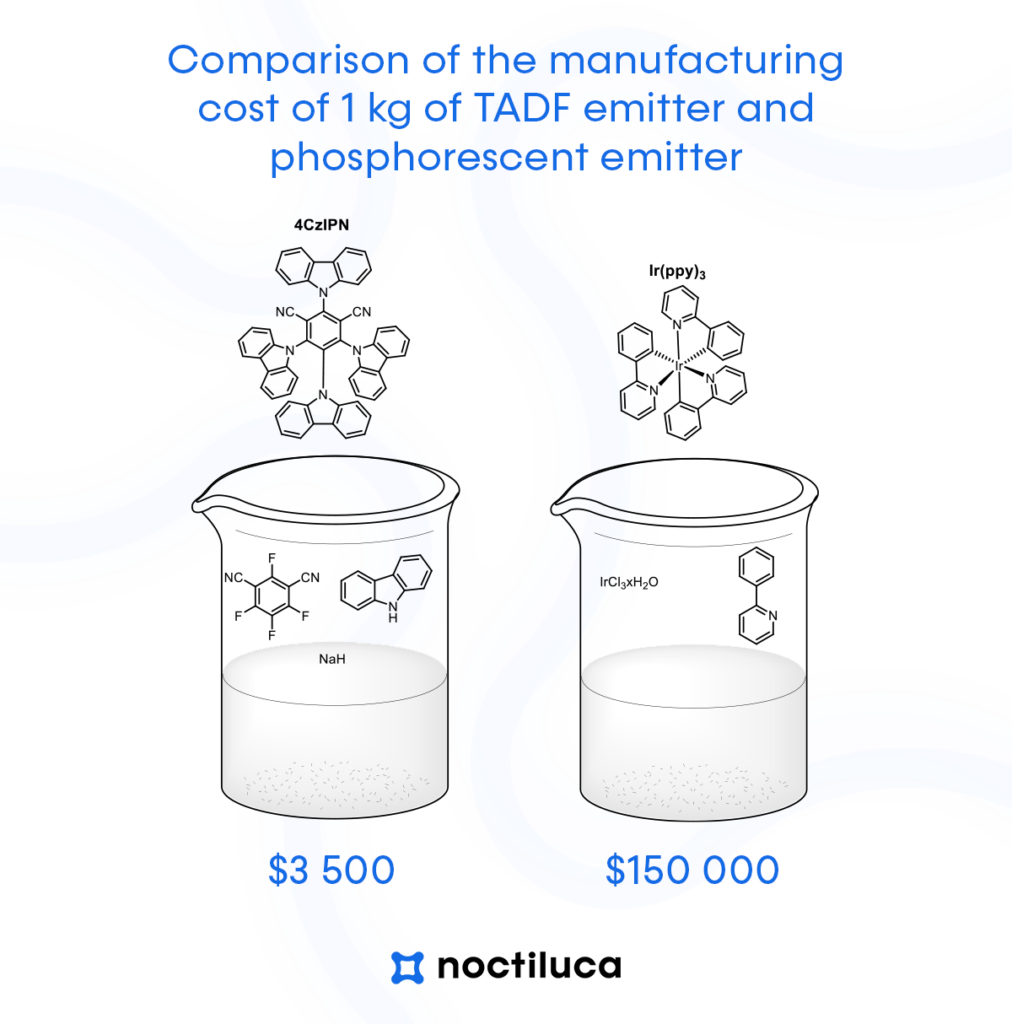
Lower manufacturing costs: TADF materials are typically easier and less expensive to produce than certain materials used in traditional OLEDs. This can lead to cost-effective manufacturing processes, which, in turn, can reduce the environmental impact associated with resource-intensive production methods.
Recyclability and disposal: TADF-based OLEDs may be more amenable to recycling due to the use of less toxic materials and simplified manufacturing processes. This can help mitigate the environmental impact of electronic waste, as recycling OLED components becomes more feasible.
Green building and design: The energy efficiency and long lifespan of TADF-based OLED lighting panels make them an attractive option for green building and sustainable design projects. Reduced energy consumption and longer-lasting lighting solutions contribute to the overall sustainability of buildings and spaces.
TADF technology is poised to revolutionize the world of OLEDs. As TADF technology continues to evolve and gain traction in various industries, we can look forward to more energy-efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly lighting and display solutions. The future of OLEDs is indeed bright, thanks to TADF.